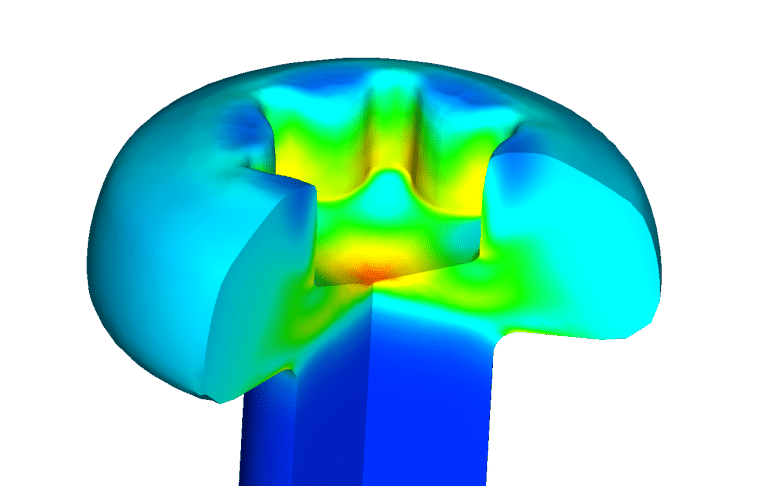
Metal Forming Simulation: FEA Based Design and Optimization for Sheet Metal Forming, Hot Forging, Cold Forming, Open Die Forging, Roll Forming, Extrusion and Heat Treatment with Ansys, Abaqus, LS-Dyna and Simufact
FEA & CFD Based Simulation Design Analysis Virtual prototyping MultiObjective Optimization
Using advanced Metal Forming Simulation methodology and FEA tools such as Ansys, Simufact Forming, Autoform, FTI Forming, Ls-dyna and Abaqus for any bulk material forming deformation, combining with experience and development have made Enteknograte the most reliable consultant partner for large material deformation simulation.
Metal Forming Simulation include Springback Compensation, Surface Defects, Cost Estimation and Phase Transformation in Sheet Metal, Hot Forge, Rolling, Extrusion, Open Die Forging and Heat Treatment Finite Element Analysis.
FEA (Finite Element Analysis) in Metal Forming
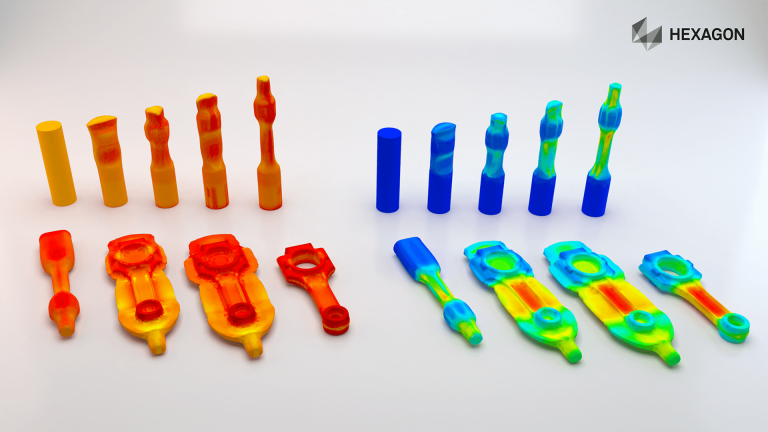
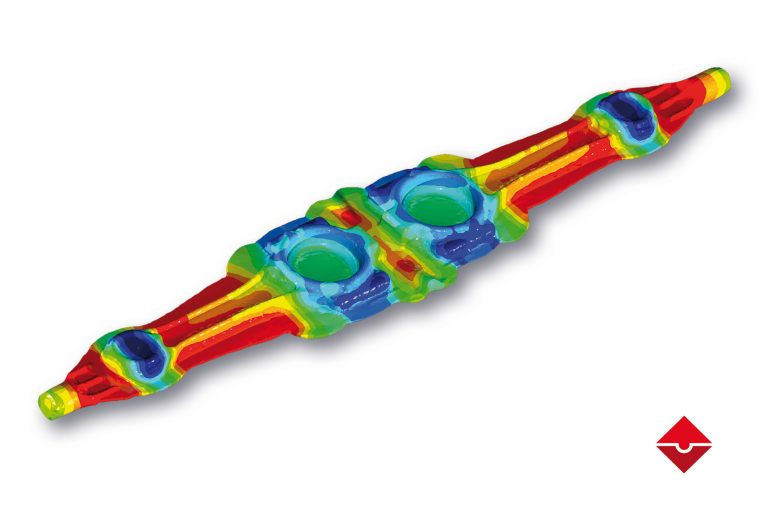
Enteknograte engineers can simulate any manufacturing process for hot, warm, and cold forging, which includes but not limited to:
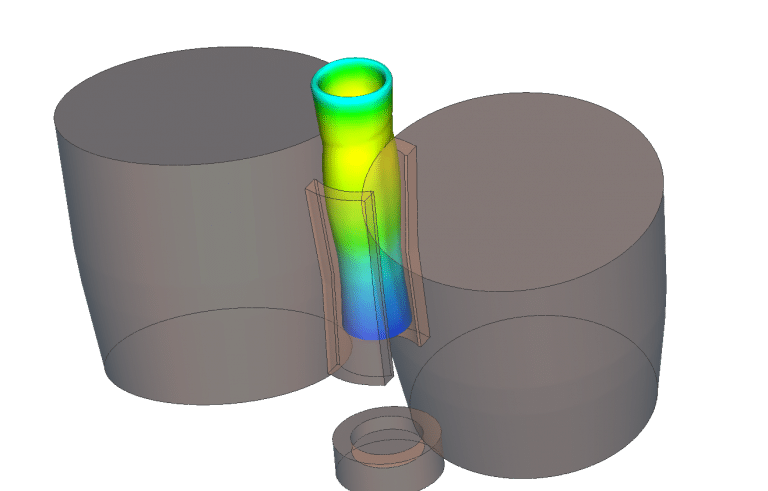
- Closed die forging
- Open die forging processes such as cogging, saddling, and other GFM processes
- Rolling for long products
- Extrusion
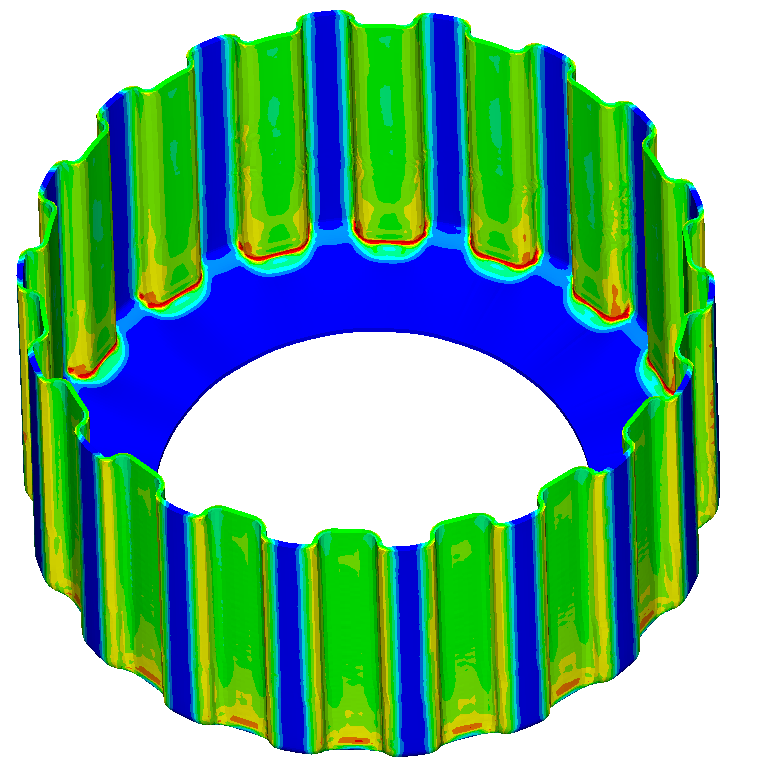
- Ring Rolling
- Cross Wedge Rolling and Reducer Rolling for pre-forming
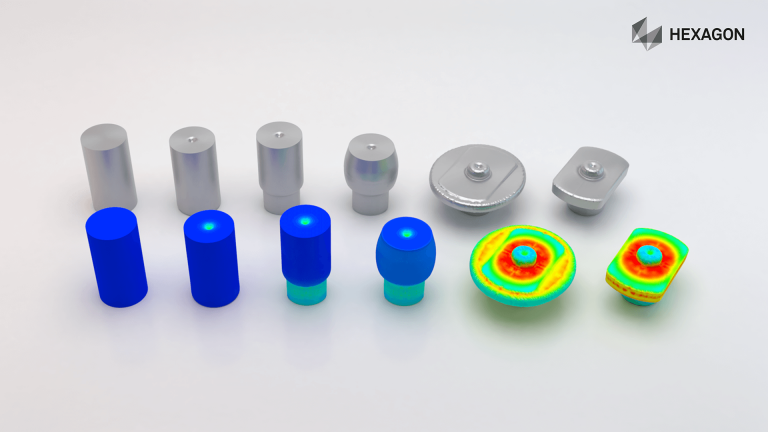
- Cold forming
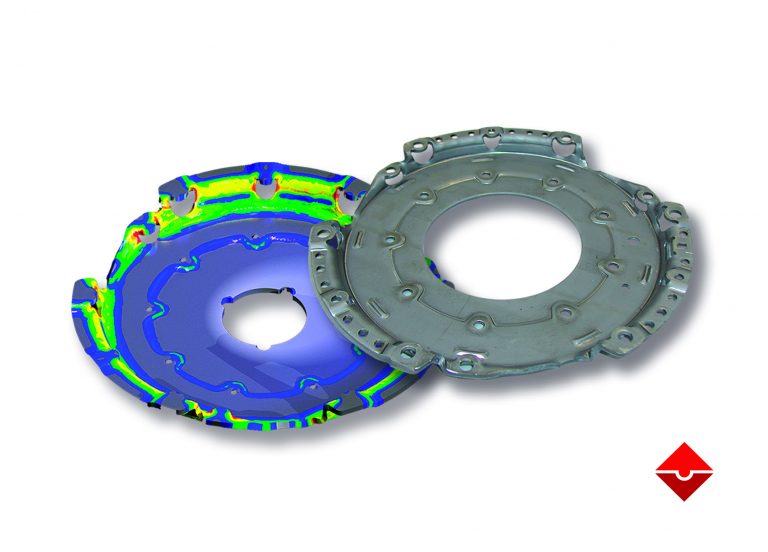
- Sheet metal forming
Phase Transformation and Thermal Effect in Metal Forming
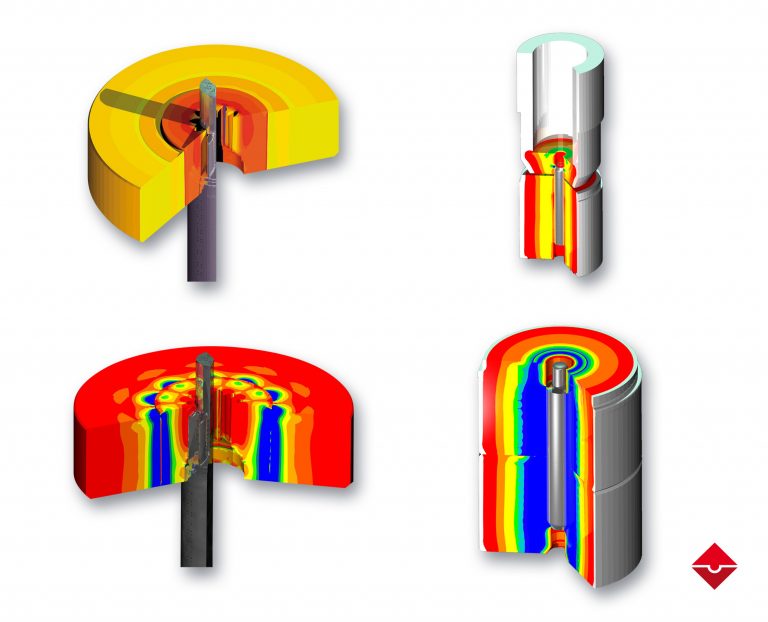
Including phase transformation and thermal effect enables us to realistically simulate the hot forming processes. These processes have become very important for the automotive industry in order to meet specific requirements regarding a higher level of crash safety and a reduction of overall weight. Detailed simulation of forming enable us to engineer components with high strength, challenging geometrical complexity and minimized springback effects. In addition, we can calculate the final part properties, such as strain-stress distributions as well as the distribution and local percentages of different material phases, such as austenite, ferrite, pearlite, bainite and martensite, including the resulting hardness distribution.
Enteknograte Simulation Features:
- Realistic simulation of hot forming and quenching processes
- Take into account phase transformation during quenching and thermal distortion after cooling.
- Stamped parts with challenging geometrical complexity and minimized springback effects
- Stamped parts engineered with targeted local strength properties
- Improved crash simulation accuracy
- Hot forming processes of ultra-high strength steels
Material Utilization
One of the most important issues in the industry is material utilization. As the price for both steel and aluminum continues to increase and more and more high-strength steels and lightweight materials are being used in the automotive industry, manufacturers continue to search for ways to optimize their use of materials. Enteknograte engineering team enable you to predict the potential of blank shape and nesting. We can efficiently calculate the optimal layout of the blank on the coil taking into consideration minimal material utilization.
Springback Compensation
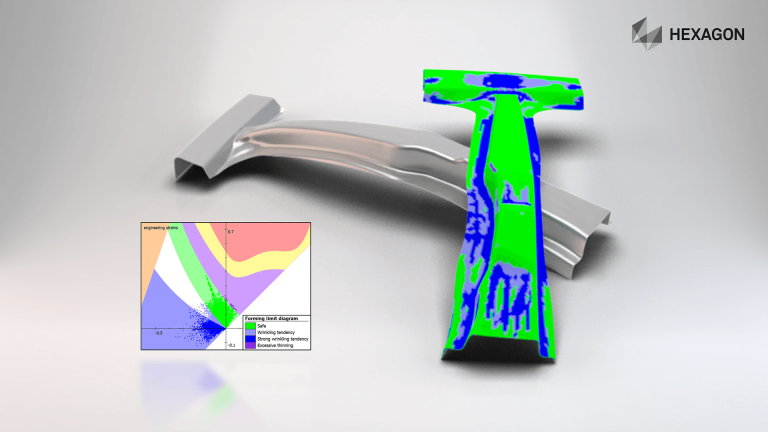
Springback compensation is carried out during the process engineering phase to improve part and tool quality before the real tryout phase begins. As a result, the process layouts realized during the early planning phases are more reliable. Robust springback compensation enables us to minimize the risk of costly changes later on in the process due to the effects of springback.
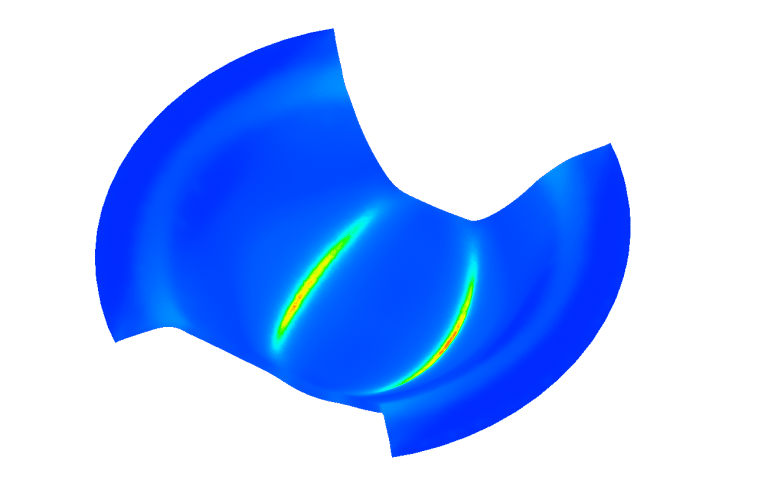
Tool Cost Estimation
We can help you to calculate tooling costs based on the defined production sequence. we can evaluate alternative production concepts and then rapidly identify the most cost-effective one. Our knowledge in FEA based design enable you to significantly reduce the time required for estimating tooling costs.
Process Planning
With special engineering methods, software and customizing ability of CAE software environment, enables us to rapidly generate and evaluate process plans. This feature enable us for increased planning reliability to meet quality and cost targets and enables the direct transfer of process plans to process engineering and validation in a short time.
Surface Defects Avoidance
Surface defects are small concave imperfections that can develop during forming on outer convex panels of automotive parts like doors. They occur during springback steps, after drawing in the vicinity of bending over a curved line and flanging/hemming in the vicinity of the upper corner of a door. They can alter significantly the final quality of the automobile and it is of primary importance to deal with them as early as possible in the design of the forming tools. As a result, during the product development process, much attention is paid to avoiding defects on surface appearance and the resulting surface quality. Enteknograte engineering team can evaluate surface defects in order to take steps to improve the surface quality with FEA based Design and optimization.
WE WORK WITH YOU
We pride ourselves on empowering each client to overcome the challenges of their most demanding projects.
Sheet Metal Forming: Advanced Finite Element Method for Industry Leading Simulation
Finite Element Simulation of Hot Forging
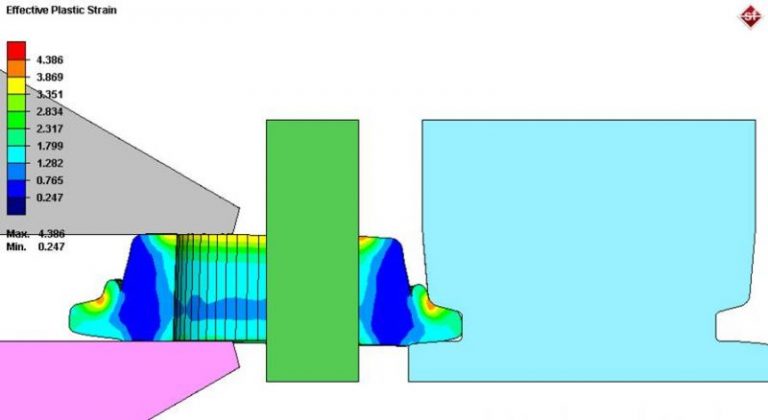
Metal Forming Process: Open Die Forging Finite Element Simulation
Cold Forming Finite Element Simulation
Finite Element Simulation of Roll Forming and Ring Rolling
Finite Element Simulation of Heat Treatment
Hard Metal: Finite Element Simulation for Mechanical Properties on the Microstructural Level
FEA (Finite Element) Welding Simulation
Acoustics and Vibration Simulation
Integrated Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning - Deep Learning with CFD & FEA Simulation
Metal Forming Simulation
Finite Element Analysis of Durability and Fatigue Life
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Heat Transfer and Thermal Analysis: Fluid-Structure Interaction with Coupled CFD and Finite Element Based Simulation